Emmanuel Orozco
Expand ChatGPT knowledge with your own information
Nov 04, 2024Table of Contents
- Why do we need to train an LLM with own data?
- Expanding LLMs current knowledge
- What is RAG?
- Preparing Data for RAG
- Embbeding models
- Code Example
- Conclusion
1. Why must we train an LLM (ChatGPT, Claude, Ollama, etc) with our private data?
To train LLMs, engineers have compressed the whole of humanity’s knowledge using public documents on the internet:
However, they have 2 big problems:
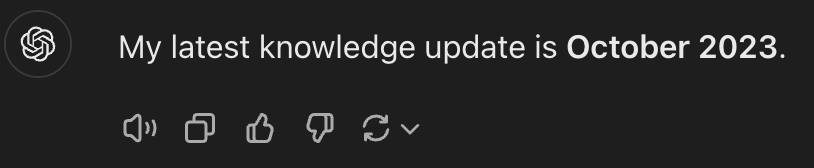
1. Outdated information
The last snapshot used to train ChatGPT is from October 2023 (now it’s November 2024), which means we lost a few months of data while generating responses.
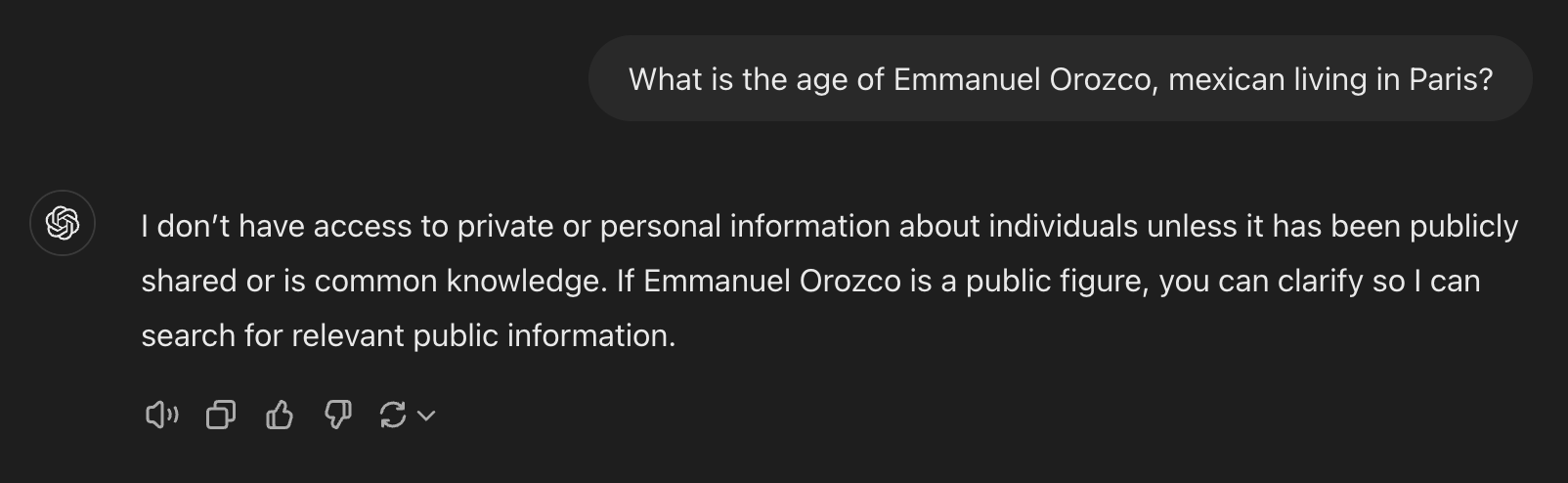
2. Lack of specialized knowledge
As mentioned, LLMs are trained with publicly available data. That means if you have private information (information on how to run a process, specific domain information, etc.), LLMs will not work as expected.
2. Expanding LLMs knowledge
So, if LLMs are outdated, what can we do about it? How can we update the information?
1. Fine Tunning
That means basically, re-train the whole model using new data (like reshaping a sculpture). We do this when we require the LLM to behave in a particular way (talk like trump, compose a new rap song).
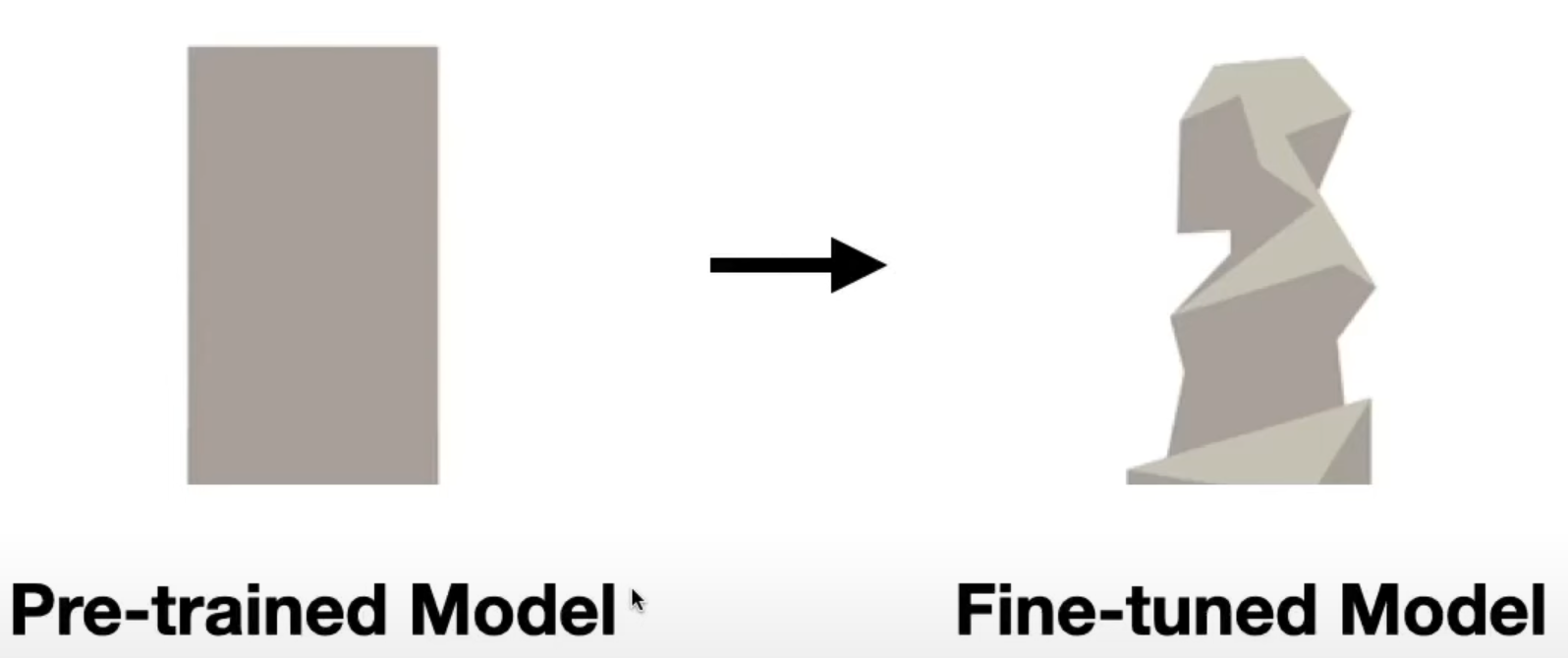
This is usually very expensive because it requires obtaining, cleaning, and processing all this new information. (requires computing and men’s power).
2. RAG
When using RAG (Retrieval augmented Generation), we don’t need to reshape the sculpture or re-train or model, we simply need to provide more information (also called context), to the LLM while making a question. Then the LLM will use this information to compute a more up-to-date answer.
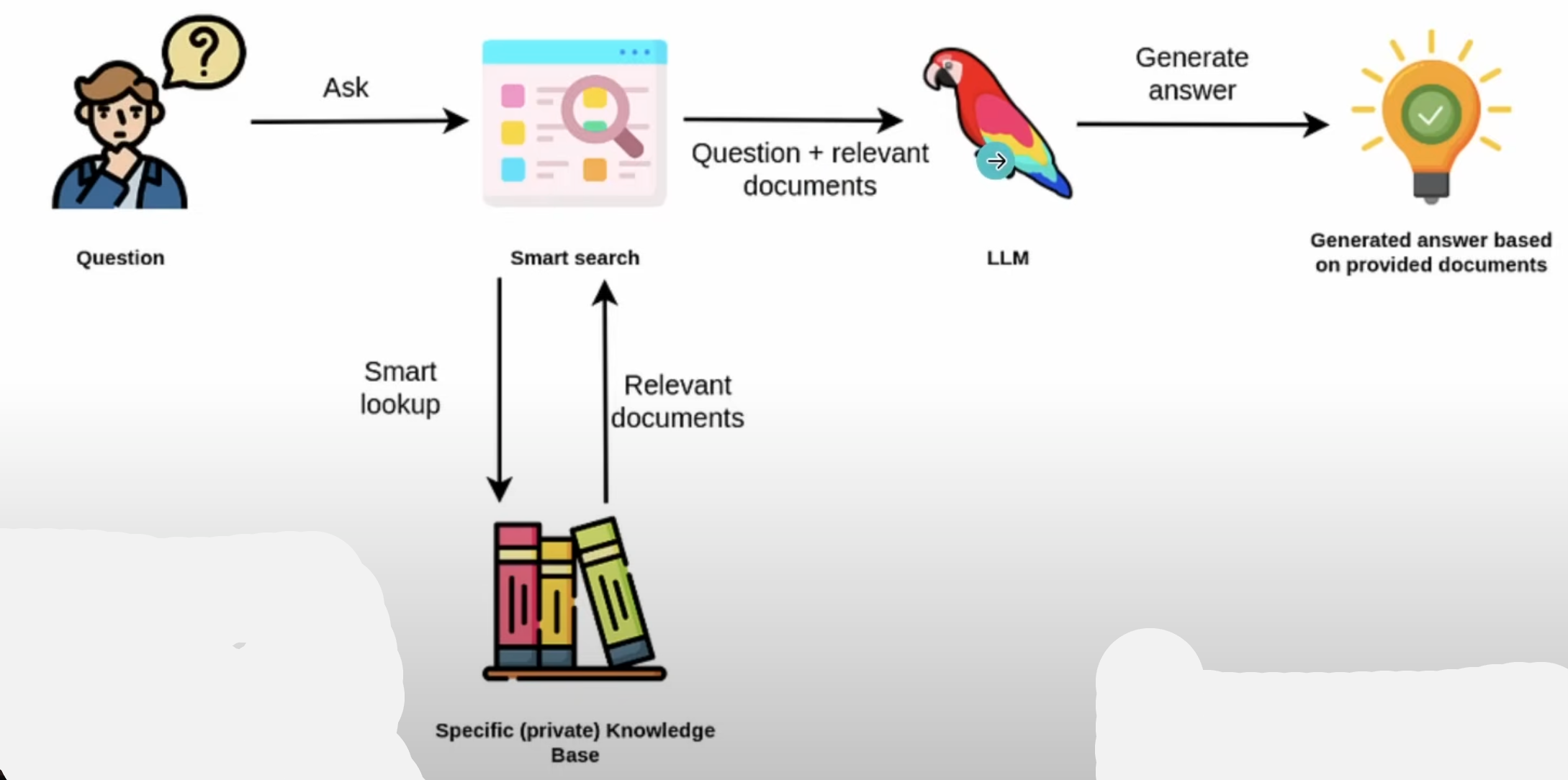
Preparing Data for RAG
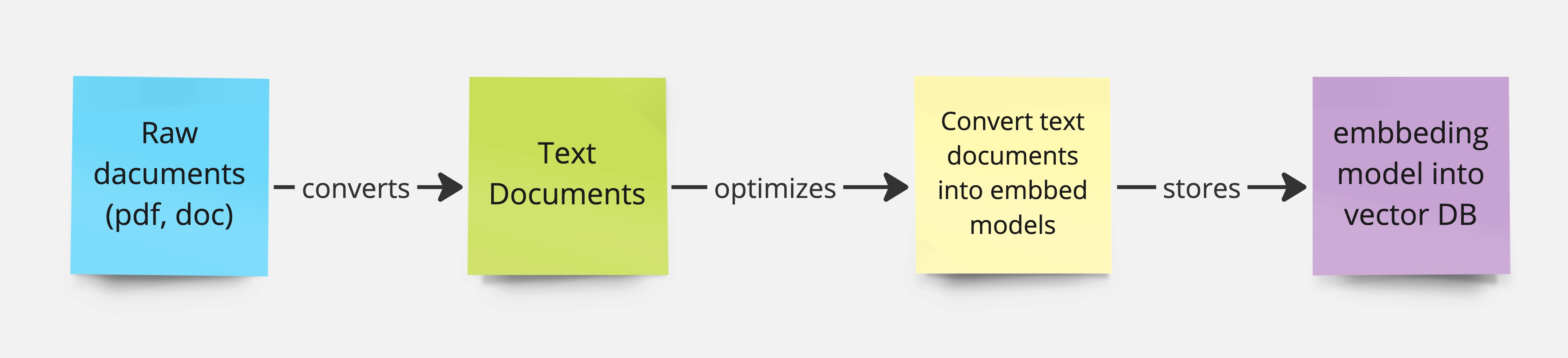
In a nutshell, to prepare our RAG we need to process our data in the following shape:
- Gather the documents with the extra information
- Convert this documents to plain text (pdf to text, image to text, etc)
- Convert this text into the embedding model (explained in the next section)
- Store the embedding data into a vector database
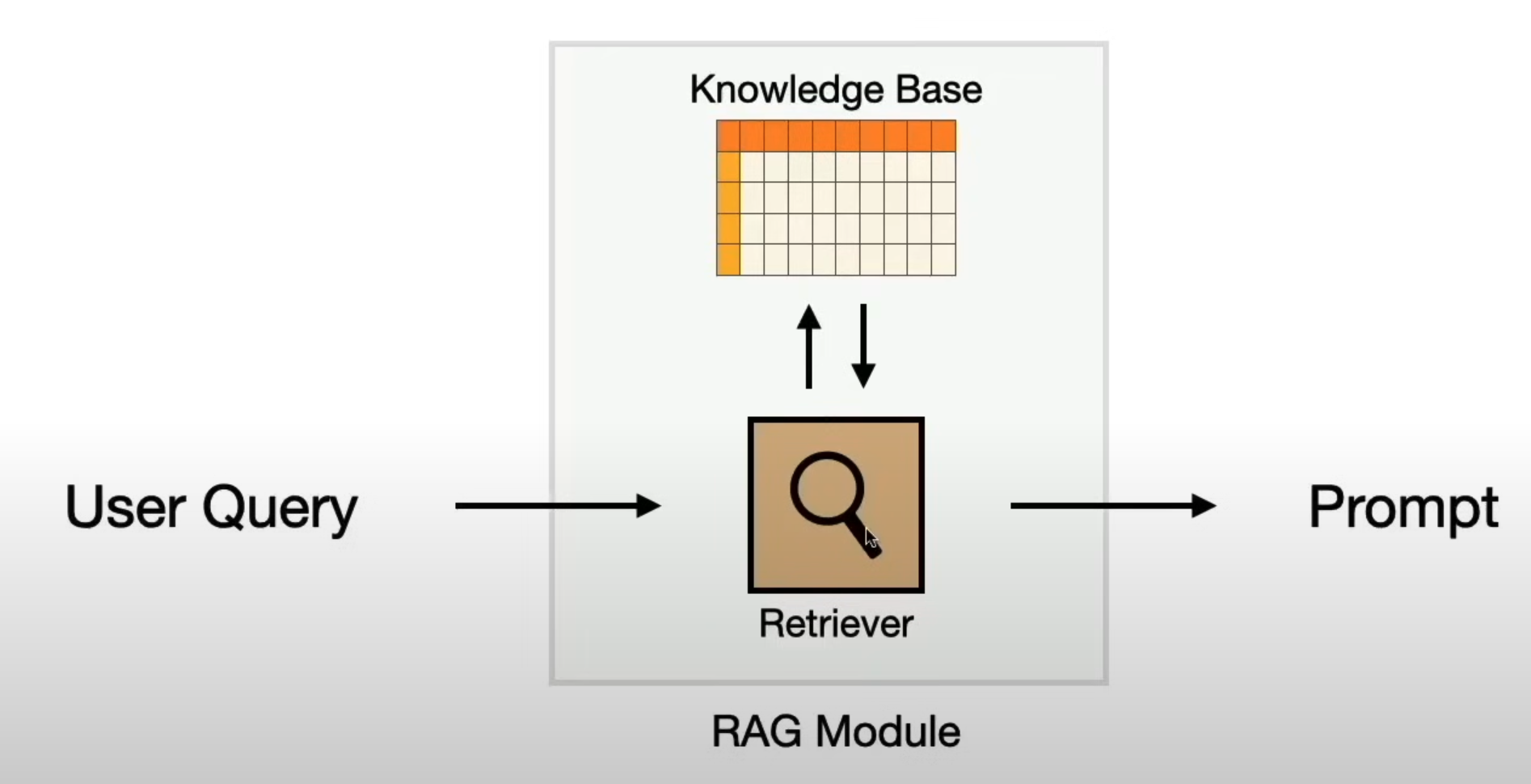
After doing this, when making a question, we need to create an RAG module that will search (in the knowledge base), for the correct aditional information and add it as context to the prompt. (retriever).
What is an embedding model and why do we need them?
We need to store our specialized information in a format that the LLM can understand. (LLMs can only understand text, not video or audio).
And we need to store this data efficiently.
Imagine you have 20,000 private PDFs of information about animal behavior (You work in a Zoo). ChatGPT does not know about this information and you want to ask GPT about a trend in this data.
Without an emmbeding model, you would need to store PDFs in database and when a question comes in to the the LLMs, look one-by-one document until you find an answer.
This takes a lot of time to compute, instead, we can use an embedding model and a vectorized database.
In an embedding model, we classify information depending on how close is to each other, using the DB records and the user question as reference.
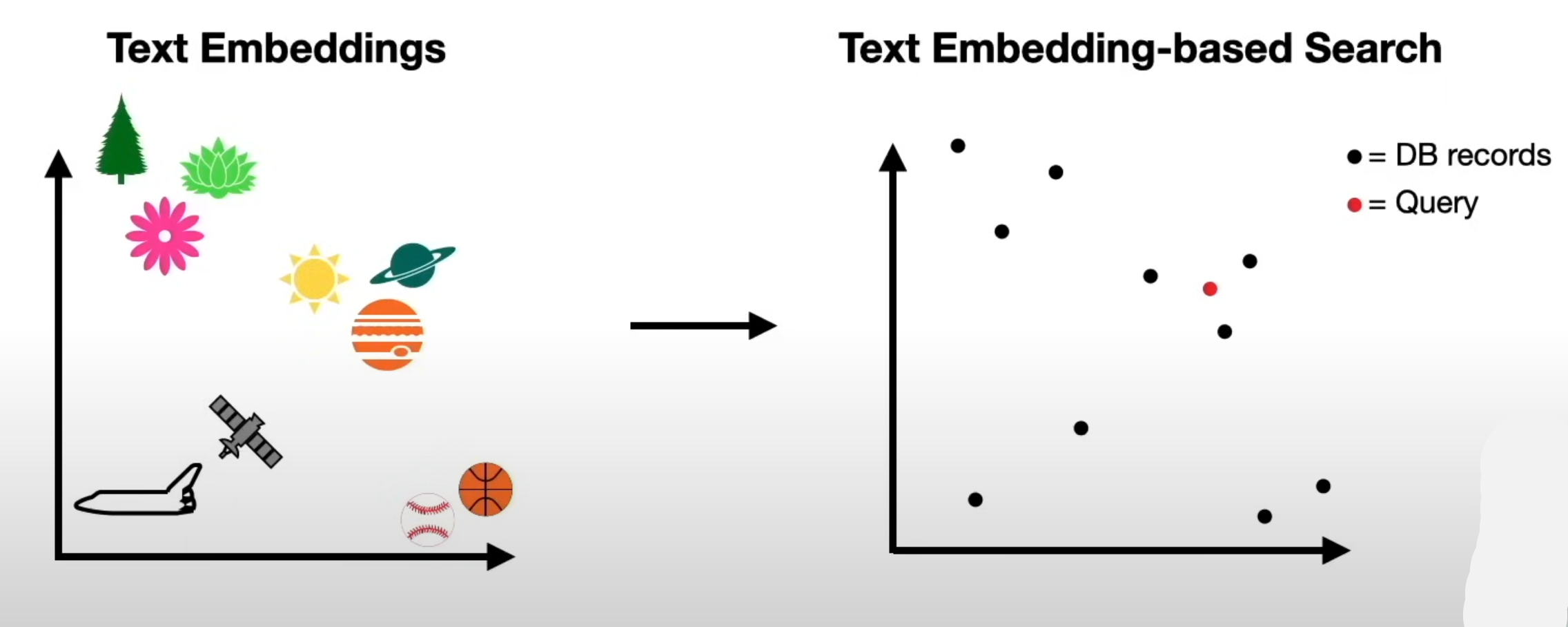
In the example above, notice how the animals, ships or celestial bodies are together.
We use an array of numbers to represent this proximity.

That way when we provide a word to this model (i.e. elephant), we don’t need to look at all documents, the embed model will automatically return the documents that contain this word (i.e. elephant will return animal, forest, big, tree).
And finally we need a vectoraised database to store this embbeded model. (Chroma and Pinecone DB are famous Vector DB engines).
Practice time
We would like to:
Help sales reps generate better email responses to their clients based on top-performing interactions with clients.
This means, that when a question comes in, we need to search what similar answers have been given before by top-sales reps in the past and generate a similar answer.
So, we need to:
- Prepare/load the data with the email interactions download it here
- Create an embedding model (proximity vectors) with email interaction data.
And when a question comes in:
- Do a similarity search
- Send a request to ChatGPT with the additional context (user question + extra documents retrieved)
- Get a response.
Here is the code step-by-step (is worth mentioning we are using LangChain, (a framework to create AI apps).
from langchain.document_loaders.csv_loader import CSVLoader
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
# 1. Load the database with the interactions
loader = CSVLoader(file_path="customer_data.csv")
documents = loader.load()
# 2. Vectorise the sales response csv data
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
db = FAISS.from_documents(documents, embeddings)
# 3. Function for similarity search
def retrieve_info(query):
similar_response = db.similarity_search(query, k=3)
page_contents_array = [doc.page_content for doc in similar_response]
return page_contents_array
#4. Send request to OpenAI with the correct documents as additional context
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4o")
template = """
You are an expert business development representative. I will provide you with a message from a prospect, and your task is to generate the most effective response.
This response should be informed by our previous successful interactions. Here is the message from the client:
{message}.
Below are examples of our best practices for responding to clients in similar situations:
{best_practice}
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["message", "best_practice"],
template=template
)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
# 5. Run user query with the right context and get response
def generate_response(message):
best_practice = retrieve_info(message)
response = chain.run(message=message, best_practice=best_practice)
return response
generate_response("What are the opening hours?")
Conclusion
Sometimes we need to train LLMs to give better responses based on our private knowledge, using a technique like RAG will allow us to do it fast and cheap while keeping the quality of the responses.
Thank you! and until the next one!